
Transformers are vital components in modern electrical systems, ensuring the efficient transmission of electricity across various networks. By converting voltage levels and providing electrical isolation, transformers play an indispensable role in every stage of power generation, transmission, and distribution. In this article, we will explore the different step-up transformer, their working principles, applications, and key differences.
What are Electrical Transformers?
Electrical transformers are used in general power distribution systems. Engineers design them to be the most common type of transformer, and they find them in various applications, from residential to commercial and industrial settings. Electrical transformers can either step-up or step-down voltage levels to meet specific needs.
Step-Up Transformer
Engineers design a step-up transformer to increase the voltage from the primary side to the secondary side. However, they achieve this by increasing the number of turns of wire on the secondary coil compared to the primary coil. Utilities use step-up transformers when they need to increase voltage for efficient long-distance power transmission.
Components of a Transformer
A transformer consists of several key components that work together to convert voltage efficiently and safely.
1. Core
Manufacturers make these windings of laminated sheets of silicon steel that make up the core and direct the magnetic flux. This composition is essential in the transfer of energy.
2. Windings
Technicians wind copper or aluminum wire for primary and secondary windings on the core. Particularly, a primary winding takes the input voltage, and the secondary winding carries the transformed voltage that the transformer produces.
3. Insulation
Engineers separate the windings by insulation material, which can be oil or solid material, like paper and varnish, to prevent short-circuiting and help cool the windings.
4. Tap Changer
Operators use tap changers to vary the voltage by changing the number of turns on the winding to maintain a constant output voltage across a range of load conditions.
5. Cooling System
Transformers use either oil or air to cool their internal components. Oil-filled transformers use oil to dissipate heat, while dry-type transformers rely on air circulation.
6. Buchholz Relay (for Oil-Filled Transformers)
A safety mechanism that measures gas accumulation or fluid flow adjustments and indicates possible internal defects.
How Does a Step-Up Transformer Work?
The basic principle behind the step-up transformer is electromagnetic induction. A magnetic field is created around the primary coil when currents are flowing through it in the form of alternating current (AC), which creates a voltage in the secondary coil. The turns in the secondary coil cause a change in voltage depending on the number of turns. Thus, by increasing the number of turns in the secondary coil, the transformer steps up the voltage, making it ideal for transmitting power over long distances with minimal loss.
Step-Up Transformer Formula
The step-up transformer increases the voltage from the primary to the secondary coil. This formula is working on the ratio between the primary and secondary windings, with the work being based on the turns:
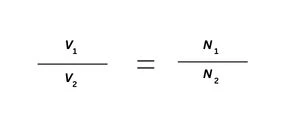
Where:
- V1 = Primary voltage
- V2= Secondary voltage
- N1 = Turns in the primary winding
- N2 = Turns in the secondary winding
For a step-up transformer, N2 > N1, meaning the secondary voltage is greater than the primary voltage.
Applications of Step-Up Transformers
Step-up transformers are essential in various electrical applications, particularly where high voltage is required for efficient energy transmission over long distances. Here are the primary areas where step-up transformers are commonly used:
- Power Plants
In power plants, step-up transformers are used to increase the voltage generated by turbines to higher levels suitable for long-distance transmission. This high voltage minimizes the losses of energy in lines of transmission, and the electricity is capable of traveling efficiently over long distances as well to reach substations.
- Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems, such as wind and solar power plants, use step-up transformers to match the voltage output from solar panels or wind turbines with the voltage levels of the electrical grid. By stepping up the voltage, these transformers help integrate renewable energy into the grid while minimizing transmission losses.
- Transmission Lines
Transmission lines rely on step-up transformers to increase voltage before the electricity is sent over long distances. Increased voltage decreases the current, minimising energy losses in the form of heat, and guarantees that the power arrives at its destination with a minimum amount of decline in power quality.
Advantages of Step-Up Transformer
Step-up transformers offer several significant benefits, making them essential for efficient power transmission:
- Efficient Long-Distance Transmission
Step-up transformers increase the voltage, which, in turn, reduces the current. It is essential in the long-distance transmission of power because the increase in voltage and the decrease in the current reduce the losses of energy, and it becomes a highly efficient process.
- Reduced Heating
By reducing the current, step-up transformers help prevent excessive heat generation in the transmission wires. Reduced current implies reduced faults lost as heat, which makes the transmission system of current more reliable and safe.
- Cost-Effective
By minimizing transmission losses, step-up transformers contribute to long-term savings. They reduce energy wastage and cut infrastructure expenses by enabling power to be efficiently delivered across long distances without involving excessive conversion of voltage along the path.
These advantages make step-up transformers a crucial part of the electrical grid, ensuring that energy is transmitted efficiently and cost-effectively across vast distances.
Conclusion
Step-up transformers are essential components in modern electrical systems, enabling efficient long-distance power transmission. By increasing the voltage while reducing the current, step-up transformers minimize energy losses and improve the overall efficiency of power transmission. They are used in power plants, renewable power systems, and transmission lines, where high voltage is essential to ensure the quality of electricity transmission over long distances. Understanding the principles behind step-up transformers, their components, and their advantages ensures that these devices continue to play a key role in shaping our electrical infrastructure for a sustainable and efficient future.
Be the first to comment