
Transformers are important elements within electrical power systems. The step-down transformer is of prime importance in ensuring the safety and usability of electricity. Although high voltages are necessary when using it efficiently in transmissions, utility companies need to lower it before it goes to homes, offices, and industries. It is here that engineers apply a step-down transformer.
The given article will provide a clear and practical explanation of what a step-down transformer is, how it functions, its formula, its components, its applications, and its benefits.
What Is a Step-Down Transformer?
A step-down transformer is a kind of electrical transformer that decreases the voltage at a higher level in the primary side to a lower voltage at the secondary side. It works by having more turns in the primary winding than the secondary winding, which produces a small output voltage.
Power distribution systems extensively use step-down transformers, where utility companies normally convert high-voltage electricity to safe levels accessible by end users.
How Does a Step-Down Transformer Work?
A step-down transformer operates by electromagnetic induction. As technicians pass alternating current (AC) through the primary winding, they generate a varying magnetic field in the transformer core. This magnetic field induces a voltage on the second winding.
Because the secondary winding has a lesser number of turns than the primary winding, the induced voltage is less. Consequently, the transformer reduces the voltage but increases the current, which makes delivery of power efficient and safe.
A step-down transformer:
- Reduces voltage
- Increases current
- Keeps the frequency constant
Step-Down Transformer Formula
The step-down transformer reduces the voltage of the primary and secondary coils. The working formula resembles the step-up transformer, except that the turns ratio is inverted:
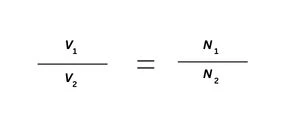
Where:
- V1 = Primary voltage (greater voltage)
- V2 = Secondary voltage (reduced voltage)
- N1 = primary winding turns (more than N2)
For a step-down transformer, N2 < N1, the voltage on the secondary is less than the voltage on the primary.
Components of Step-down Transformer
A step-down transformer has several very fundamental parts that combine to enable a safe processing of high voltage into lower and usable levels. Every part has a certain role in the efficient and reliable functioning.
-
Core
The core offers an internal route to the generated magnetic flux when operating a transformer. It consists of laminated silicon steel to minimise energy losses to eddy current and hysteresis. The core promotes effective magnetic coupling of windings.
-
Primary Winding
High-voltage input supply is connected to the primary winding. It has more turns than the secondary winding, and hence the transformer can reduce the voltage when operating it.
-
Secondary Winding
The secondary winding provides the lower output voltage. Because the turns per winding are fewer than the primary winding, the voltage induced in this winding is small enough for appliances and equipment to use safely.
-
Insulation System
Insulation is used to ensure that windings are separated from one another and the core. It eliminates short-circuiting of electricity and improves security. Paper, varnish, and oil are common insulation materials in oil-filled transformers.
-
Cooling System
During operation, the cooling system removes heat. Engineers design step-down transformers to be cooled with air (dry-type) or oil (oil-filled) to secure proper operating temperatures that are safe.
-
Tap Changer
Tap changers regulate the voltage by increasing or decreasing the number of active turns in the winding. Users utilize them to regulate the constant output voltage during load changes.
Types of Step-Down Transformer
Engineers can typically divide step-down transformers into three types, according to the design and the ability to control the voltage. Each type serves certain electrical applications based on voltage needs and system flexibility.
-
Single-Phase Step-Down Transformer
A single-phase step-down transformer steps down DC voltage from the primary winding to a second winding through a single-phase AC supply. It consists of a primary and secondary tube wound around a ferromagnetic core. The high-voltage input links to the primary winding, and the low-voltage output links to the secondary winding. Utility companies often use these transformers in residential and commercial places because they need to safely transform the high transmission voltage into everyday use. They also commonly appear in power distribution systems and other electronic devices because of their design and quick performance.
-
Center Tap Step-Down Transformer
A center tap step-down transformer is a type of transformer that has a second winding with a center tap and is divided into two equal-voltage portions. This design enables the transformer to supply more than one voltage output using one winding. The center tap is flexible, giving the possibility of having the secondary winding linked in series or parallel, depending on the voltage needs. A common application of these transformers is in a power supply circuit where varying voltages of various components are needed in the same circuit.
-
Multi-Tapped Step-Down Transformer
A multi-tapped step-down transformer is a transformer that has a multi-tap connection to the secondary winding so that the user can choose the level of output voltage. This kind is very flexible in nature, with the voltage adjustable to meet the demands of a particular application. Multi-tapped transformers are very common in factories with various machines having varying operating voltages. The transformer can be adjusted simply by choosing the correct tap to ensure that it fits into a variety of dynamic electrical systems.
Applications of Step-Down Transformers
-
Residential and Commercial Buildings
Homeowners and commercial property managers commonly use step-down transformers to get premium voltage electricity generated and sent through the power grid into levels that can be used safely and efficiently. Household appliances and office equipment run on significantly lower voltages. So, these transformers ensure safe operation and prevent electrical destruction of devices.
-
Power Distribution Systems
Engineers use step-down transformers in the power distribution systems to transform the voltage in the transmission levels to the voltage in the distribution levels. Lastly, they deliver electricity to consumers. Such a controlled decline enables utility companies to efficiently deliver electricity throughout the city and town without compromising the consistency of voltages and system safety.
-
Electronic Devices
Manufacturers require step-down transformers in electronic hardware like phone chargers, adapters, and power supplies. Such devices need low and accurate voltage, and engineers use transformers to prevent excessive heating of the delicate electronic parts, electrical short action, and breakdowns.
Advantages of Step-Down Transformers
-
Improved Electrical Safety
The step-down transformers offer one of the most important benefits in the form of improved electrical safety. They minimize high voltage to safe levels, preventing users and equipment from being shocked and damaged by insulation.
-
Stable and Regulated Power Supply
Step-down regulators offer constant and smooth voltage. This will assist in avoiding voltage variation that tends to overload circuits and destroy electrical appliances, thus enhancing reliability.
-
Cost Efficiency and Equipment Protection
Step-down transformers minimize energy wastage by delivering electricity at the right voltage levels, minimize equipment breakages, and decrease system maintenance and replacement expenses. This renders them an affordable solution in long-term power distribution.
Conclusion
Step-down transformers are needed to ensure safe reduction of high transmission voltage to usable levels in electrical systems. They promote consistency in voltage regulation, equipment protection, and general performance in improving the distribution of power in homes, industries, and electronic devices. Step-down transformers are important aspects of modern power infrastructure due to their effect on electrical safety and the low operational cost.
Be the first to comment